Http vs. Https
HTTP vs. HTTPS: The Difference in Performance and Security
With HTTPS becoming the standard, it's essential to understand what exactly it means to have an HTTPS connection and how it affects your performance. If you want to know the differences between HTTP vs. HTTPS and how your user's browser handles these connections, keep reading!
It's often believed that having an HTTPS connection can significantly slow down your site because of the additional encryption overhead.
Still, different studies have shown that saving a few milliseconds didn't outweigh the increased level of security that SSL affords.
However, with HTTP/2, HTTPS is only getting faster, but more on that later.
What Is HTTP?
HTTP, or Hypertext Transfer Protocol, had long been the standard protocol for communication on the World Wide Web.
It's been the foundation of data communication on the Internet.
Think of it as the prescribed order and syntax for transferring data over a network.
Most information sent over the Internet – including website content and API calls – uses the HTTP protocol.
There are two kinds of HTTP messages: requests and responses.
Requests are generated by a user's browser.
For example, if a user clicks on a hyperlink, the browser will send a series of HTTP requests for the content that appears on that page.
These requests go to an origin server or a proxy caching server.
Then the server will generate an HTTP response, which is the information that shows on search results.
What Is HTTPS?
Since its first introduction, HTTPS has kept on spreading like wildfire.
It is now backed by Google and other big names in the industry, making it the standard protocol for browsing the web today.
Why? Because of its security!
It's the padlock you see near the URL bar, meaning that any information sent between the site and your browser is secure and can't be intercepted by someone else.

Nowadays, 95% of websites on Google use HTTPS.
However, HTTPS is not yet the official ruler of the Internet.
After the pandemic started, Google took security seriously, pushing for 100% encryption (which is still in full swing.)
As a result, almost all websites you see come with a padlock.
So, encrypted websites run the show whether you search via Bing or Google.
How Are HTTP and HTTPS Different?
There are a few key differences between HTTP vs. HTTPS that can impact your website's performance, speed, security, and SEO.
For one, HTTPS is getting faster because it uses the newer HTTP/2 protocol, allowing faster loading times.
This HTTP vs. HTTPS test offers a visual comparison of the load times for the unsecure and encrypted versions of the same page.
The results speak for themselves.
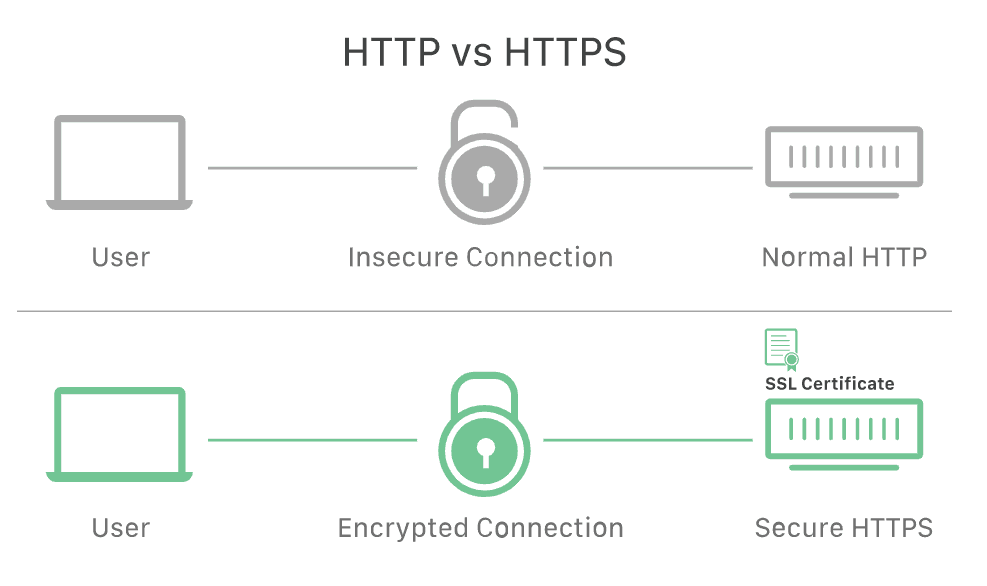
Additionally, HTTPS is more secure than HTTP since it encrypts data using SSL/TLS.
It provides SSL or TLS Digital Certificate, which secures the communication between server and client.
So, while HTTP transfers data in plain text, HTTPS transfers data in encrypted text.
This can help prevent technical SEO issues like malware attacks or data breaches.
Finally, Google prefers HTTPS websites, so switching to HTTPS can give you a slight ranking boost in search results.
This has been confirmed as a ranking factor since 2014, so getting a small ranking boost is a good reason #1 for switching to HTTPS.
HTTPS Helps Authenticate Web Servers
It's no secret that HTTPS can help improve your website's ranking in search results.
But how exactly does it do this?
As I have repeatedly mentioned above, HTTPS helps authenticate web servers.
This means that when someone tries to access your website, they can be sure that they're actually connecting to the server that you intended them to connect to.
Just like an ID card confirms a person's identity, in this case, a private key confirms the server's identity.
When someone navigates to a website, the private key matches with the public key in a website's SSL certificate, proving that the server is actually the legitimate host of the website.
This prevents or helps block several attacks that are possible when there is no authentication.
To Switch from HTTP to HTTPS
- Purchase an SSL certificate: Many web hosting companies (like GoDaddy, for example) sell SSL certificates. However, research before making your purchase.
- Install your SSL certificate: Follow the instructions the web hosting service provides
- Update all your internal links from HTTP to HTTPS: If you notice any link still points to the HTTP version of your webpage, you have to update it directly in the code.
- Redirect from HTTP to HTTPS: You can manually redirect to ensure that the browser points to the HTTPS version of your webpage.
Conclusion
When it comes to differences between HTTP vs. HTTPS, the latter is more secure and offers better performance due to that reason.
This means that your website's traffic will be encrypted, making it more difficult for hackers to intercept data.

Additionally, HTTPS can improve your website's ranking by reducing the amount of time it takes to load pages.
This is because HTTPS uses a compression algorithm that compresses data before it is sent over the network.
So, if you're looking for a more secure and faster website, switching to HTTPS is the only way to go!

