Hreflang Mistakes Costing You Traffic (How To Fix Them)
In the world of search engine optimization, there are many different factors to consider when trying to determine how your website ranks on Google, Bing, or any other search engine.
One of the most overlooked and important factors to global SEO success is something called hreflang markup.
Hreflang markup allows you to tell search engines what language your content is in, as well as which countries it should be translated into if it isn’t already localized for that area of the world.
What Is Hreflang, and Why Is It Important?
Hreflang is an HTML tag that tells Google which language you’re writing your content in multiple languages.
It’s important for global SEO because it helps Google serve your content to the right audience.
If you’re not using hreflang tags, you could be missing out on a lot of traffic.
Using them tells Google and other search engines which page and in which specific language should be shown to the users searching depending on their location and language settings.
For example, for different web pages targeting users in the US, Canada, and Australia, you need to specify which website pages search engines should show in the localized search results.
The Most Common Mistakes

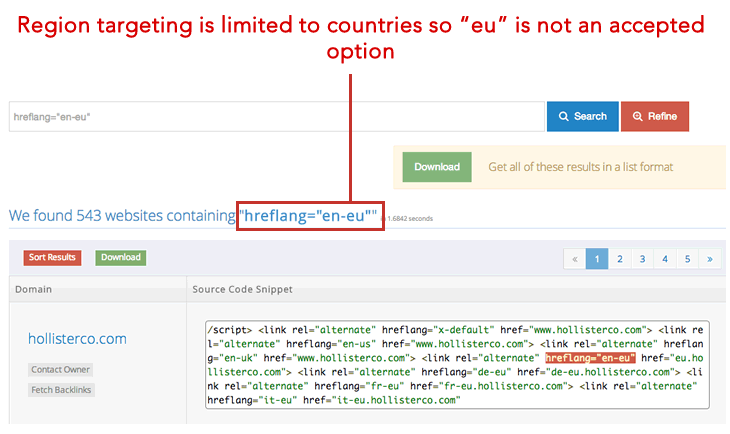
Example #1: Issues with Hreflang Values
The first of the many hreflang mistakes we are going to mention in this article is using the wrong hreflang values or hreflang attributes.
This can be a result of incorrect international SEO analytics or simply not knowing what is hreflang code.
A hreflang checker can help you ensure that your hreflang attributes are correct and that you’re not inadvertently excluding any languages.
You have to use ISO 639-1 format for the language code and ISO 3166-1 Alpha 2 format for the country code.
Of course, there will be typos every once in a while since these mistakes can be easily made by accident.
Simply double-check the hreflang tag and fix this error when needed.
Example #2: Missing/Incorrect Return Links
Another serious hreflang annotations mistake worth mentioning is forgetting to include return links or using the wrong return tags.
According to Google: “When using an Hreflang tag, if page X links to page Y, then page Y must link back to X.”
What this means is: you have to point search engines in the right direction so that it can index all your pages.
If the hreflang attribute is pointing to a page that doesn’t exist, is redirected, or you are using relative URLs, then the search engine can dismiss, ignore, or even misinterpret the link provided.
That’s why it’s important that the code is consistent across all pages included in the Hreflang implementation and that all indicate they are live.
Example #3: Incorrect or Missing Canonical Tags
One of the most critical hreflang mistakes is incorrect or missing canonical tags.
This can cause serious problems for your website, as it can confuse search engines and lead to duplicate content issues.
Canonical tags tell search engines which version of a page is the original and should be used when there are multiple versions of a page (for example, if you have an English and French version of the same page).
If your canonical tags are incorrect or missing, it’s important to fix them as soon as possible.
Example #4: More Than One URL Is Specified
If more than one URL is specified for the same language or country, Googlebot will ignore all of them.
Why?
Because it doesn’t know which page code to index for this language version.
To fix this mistake, you need to remove all conflicting hreflang URLs and ensure you only have one URL specified for that particular language and country.
Additionally, it is important to make sure that there are no conflicting or invalid Hreflang URLs present if you don’t want to hurt your website ranking.
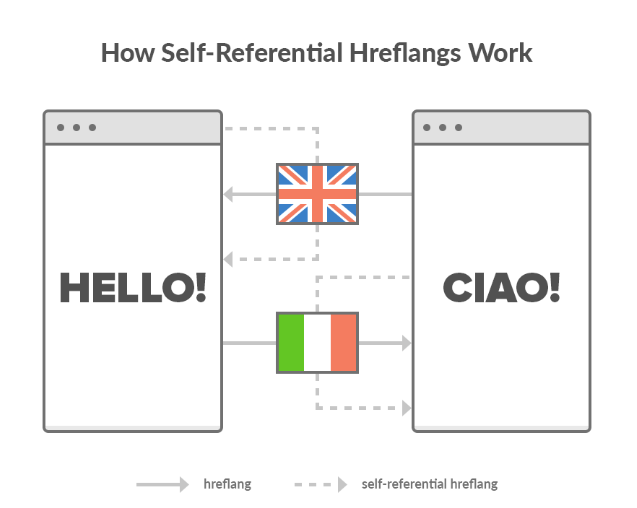
Example #5: Missing Self-Referencing Hreflang Tag
One of the most common hreflang mistakes in this section is forgetting to add self-referencing hreflang tags.
Google states, “Each language version must list itself AND all other language versions.”
Translation: Every page should have a self-referential hreflang tag to point back to itself.
If that’s missing, it can index incorrectly your pages, costing you traffic.
A study from SEMrush found that if a website has a conflict within a page source code, in 96% of cases, it was due to a missing self-referencing hreflang.
That means that you can ignore or interpret those hreflang annotations incorrectly.
To fix this issue, ensure you include the page’s URL and language code in your hreflang attribute.
Conclusion
If you’re not using hreflang tags on your website, you could be missing out on a lot of traffic.
Not to mention, you could also be inadvertently damaging your international SEO success.
The good news is that there are some easy ways to identify and fix the most common hreflang mistakes.
By using a hreflang checker and paying attention to your global SEO analytics, you optimize your website for international audiences.





