What is Keyword Cannibalization? (And How to Fix It)
Keyword cannibalization is the term used to describe how two or more pages on your website are targeting the exact same or similar keywords and thus, taking away traffic from each other and weakening their rankings because there’s no clear winner between them.
In this article, you’ll learn what keyword cannibalization is, why it happens, what you can do about it, and how you can identify it to fix it on your site(s).
Why Does Keyword Cannibalization Happen When Targeting the Same Keyword?
This happens when you have different pages with content targeting similar keywords, but they don’t have internal links pointing back to each other. Having distinct category pages that target different keywords relevant to your products can help prevent keyword cannibalization.
Instead, these multiple pages get caught in a vicious cycle of trying to target more of the same keyword(s). Optimized category pages can help avoid keyword cannibalization by ensuring that search engines can identify and rank the most relevant page for user queries.
After all, keywords are one of the most important elements of an online search, and sometimes, you need the help of a freelancer to do the job for you.
The more keywords two pages target and try to rank for, one of those multiple pages ends up ranking lower in search results than it should because it’s like competing against itself.
To avoid keyword cannibalization or any kind of keyword confusion between two or more pages on your site, ensure that all your related content has some type of cross-linking between them.
Identifying Keyword Cannibalization Using Google Search Console
1. Ranking URL Keeps Changing
When your ranking URL keeps changing, it could be a sign that you are keyword stuffing or cannibalizing.
When you have multiple pages on your site but want them all to rank for one term or phrase, there’s a good chance that Google sees two different pages trying to rank for the same thing and penalizes both.
Since the URL positions in the search results frequently fluctuate, the user’s experience is negatively impacted, leading to lower search rankings.
This is especially true when one page converts users at a much higher rate than the other.
2. You Notice a Search Engine Rankings Fluctuation
This fluctuation happens alongside URLs changing.
You probably have noticed that your ranking position for a specific keyword keeps fluctuating.
Suppose that one page ranks higher for a high-volume term than another, yet the page’s overall search intent and quality seem to be lacking.
This also means that your organic traffic can fluctuate if one of the URLs ranks in a higher position for targeted keywords.
3. You Have Great Content and Links But Aren’t Ranking
Suppose you’ve recently put effort into building links, getting backlinks, and creating great content but aren’t seeing any increase in rankings.
So, if someone is searching for “link building” and sees two articles from your website with the exact keyword in the title, they will be pretty confused, and so will the search engine. This often happens when multiple pages serve the same search intent, leading to keyword cannibalization.
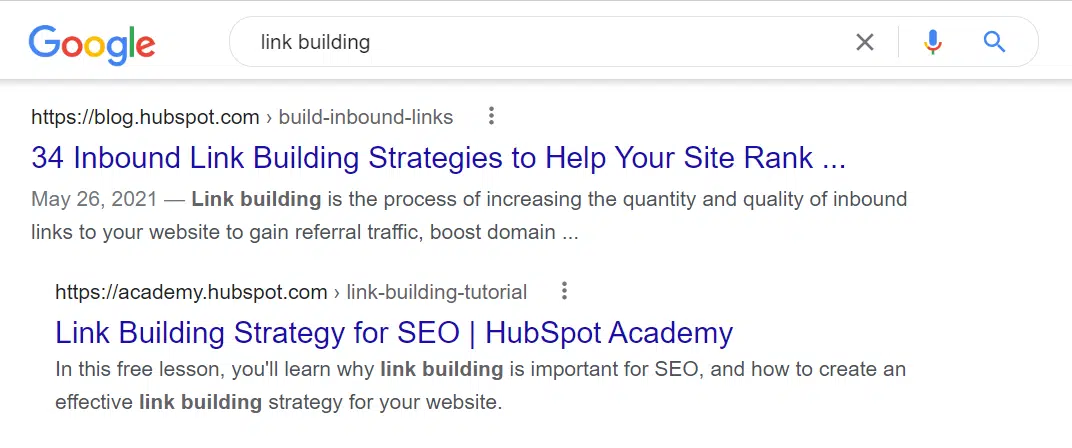
This is a good sign that there are issues with keyword cannibalization.
Sometimes, you may even find that merging duplicate articles onto one page makes sense.
But we will explain the fixes in more detail below.
4. You Notice That the Wrong URL is Ranking
If you have several similar pages with duplicate content, your chances of ranking for any given keyword in the search results are dramatically reduced.
That’s because search engines have a bias towards a single version of any given page being ranked.
This results in search engines pushing down all but one version of that preferred page when they crawl it.
You may also find that sometimes an old URL ranks for your desired keyword.
It could be an old piece of content, but it’s irrelevant compared to the new article/blog, and you don’t want it to rank anymore for a specific keyword.
5. Using Google Search Console
Google Search Console (GSC) is a powerful tool that can help you identify and fix keyword cannibalization issues on your website. Here’s how to use GSC to detect and resolve keyword cannibalization:
Sign in to Your Google Search Console Account: Start by logging into your GSC account and navigating to the “Search results” section.
Review Search Queries: Scroll down to see a list of search queries (keywords) for which your website has earned clicks and impressions.
Identify Suspect Keywords: Click on a keyword that you suspect may be causing cannibalization issues.
Analyze Ranking Pages: In the “Pages” tab, look for multiple URLs that are ranking for the same keyword.
Evaluate Content Similarity: Analyze the pages to see if they have similar content, titles, or meta descriptions.
Confirm Cannibalization: If you find multiple pages targeting the same keyword, it’s likely that you have a keyword cannibalization issue.
To fix the issue, you can use GSC to identify the preferred page and then use a 301 redirect or canonical tag to consolidate the ranking power of the other pages. This helps ensure that search engines recognize the most relevant page, improving your search results and overall SEO performance.
Understanding the Impact of Keyword Cannibalization
Keyword cannibalization can have a significant impact on your website’s search engine rankings and traffic. Here are some ways in which multiple pages can harm your website:
1. How Multiple Pages Can Harm Your Website
When multiple pages on your website target the same keyword, it can confuse search engines and make it difficult for them to determine which page is the most relevant. This can lead to:
Lower Search Engine Rankings: Search engines may struggle to decide which page to rank, resulting in lower rankings for all the pages involved.
Reduced Traffic and Conversions: With diluted rankings, your pages may receive less traffic, leading to fewer conversions.
Increased Bounce Rates and Decreased User Engagement: Users may land on less relevant pages, leading to higher bounce rates and lower engagement.
2. The Consequences of Keyword Cannibalization
Keyword cannibalization can have serious consequences for your website’s SEO. Some of the consequences include:
Diluted Page Authority: When multiple pages compete for the same keyword, the authority of each page is diluted.
Reduced Link Equity: Link equity is spread thin across multiple pages, weakening the overall SEO strength.
Decreased Search Engine Rankings: The confusion caused by multiple pages targeting the same keyword can lead to lower search engine rankings.
Increased Competition from Other Websites: With your pages competing against each other, external competitors may have an easier time outranking you.
How To Fix Keyword Cannibalization?
You can always prevent cannibalization from happening in Google Search by using great keyword research tools. Cataloging web pages alongside their target keywords as part of a content audit process can help identify and address keyword cannibalization.
Targeting different search intents—such as informational, transactional, or commercial—can also fix keyword cannibalization by ensuring each page attracts different types of user queries.

However, if the issue has already occurred, there are some keyword cannibalization solutions you can try.
1. Merge The Cannibalizing Articles Into One Content.
Once you’ve identified pages that are likely cannibalizing each other, merge them into a single page and make sure they link to each other internally.
A good way to start is by having one page focus on your broadest target keyword and then make another page more specific from there.
2. Delete The Content That Isn’t Relevant Anymore
Another way to fix keyword cannibalization is by removing old content that doesn’t fit within your updated SEO strategy.
It’s fairly common for old content to still rank, even when it doesn’t provide value anymore.
So identify what isn’t working and let it go to improve pages ranking.
3. Changing The Internal Linking Of Your Website
The general rule of thumb when it comes to internal linking is: don’t link duplicate content or pages targeting the same or similar keywords.
Your goal with internal linking should be a cohesive user experience, not hiding duplicate content or spamming out irrelevant keywords in an attempt to rank for them.
Ensure all relevant pages are correctly linked together and contain highly relevant keywords and search terms.
Also, try changing the internal linking so that less essential content links to the content can be prioritized.
This fix helps the search engine to understand which content is more important for the readers and rank them in the search results accordingly.
4. Change Inbound Link Requests
Inbound links are a key factor in getting organic search traffic.
If you notice that some of your old articles receive more inbound link requests than others, especially from very influential websites or an authoritative source page, you might have an issue.
To fix it, track your backlinks and contact the webmaster requesting they delete the links to the wrong page altogether or link it to the new (relevant) article.
In this case, you will be exchanging the old links you don’t want anymore with the new ones you want to prioritize. This ensures the correct page ranks higher for the intended search query.
Preventing Keyword Cannibalization
Preventing keyword cannibalization requires a strategic approach to content creation and optimization. Here are some tips to help you prevent keyword cannibalization:
Conduct Thorough Keyword Research: Identify unique and relevant keywords for each page to ensure that no two pages target the same keyword.
Create High-Quality, Unique Content: Develop unique content for each page that targets a specific keyword, ensuring that each page serves a distinct purpose.
Use a Clear and Consistent Hierarchy: Organize your website with a clear hierarchy to help search engines understand the structure and importance of your pages.
Implement Internal Linking: Use internal linking to help search engines understand the relationships between your pages and to distribute link equity effectively.
Regularly Monitor Your Website: Keep an eye on your website’s search engine rankings and traffic to identify potential keyword cannibalization issues early.
By following these tips, you can prevent keyword cannibalization and ensure that your website is optimized for search engines, leading to better search engine rankings and improved user experience.
Conclusion
To conclude this blog post, keyword cannibalization can harm your SEO efforts.
The easiest way to prevent that is by being proactive and not having multiple pages to target the same keyword.
You need to write a page content plan—basically, a chart that shows which pages include which keywords and how they differ from one another.
By having your information organized into these bite-sized chunks, you can easily prevent keyword cannibalization from occurring.
After all, there’s no point in investing time and money into creating one piece of content if you’re just going to duplicate it by mistake.





