Multilingual SEO: Should You Target by Country or Language?
If you want to make the most of your multilingual SEO efforts, the question of whether to target by country or language isn’t as simple as it may seem.
To maximize your reach and traffic, you’ll need to determine which approach makes the most sense, depending on your goals, your audience, and how you plan to launch your marketing campaign.
This article will walk you through both approaches so that you can choose which one is best for your business.
But first, keep in mind that a well-planned multilingual SEO strategy is crucial for expanding your online visibility in different language markets.
What Is Multilingual Website SEO?
Multilingual SEO is the process of optimizing a website to rank in search engines for users in multiple languages.
However, relying on Google Translate for translating web pages and optimizing content for multilingual SEO has its limitations. Automated translation tools lack the nuances required for accurate and effective communication. That make human translators essential for achieving high-quality translations that resonate with diverse audiences.
It involves translating content and adapting SEO practices – such as keywords, meta descriptions and URL structure – so search engines can show the right version of a site based on a user’s language preference.
For example if your website is for English speakers but you also have a Spanish version, multilingual SEO ensures Spanish speakers find the Spanish content in search results. This helps businesses reach international audiences, increase organic traffic and improve user experience for non-native speakers. By managing language specific SEO factors you can expand your reach, drive conversions and connect with audiences in different regions.
How does it differ from international SEO?
The main difference between multilingual SEO and international SEO is the audience and site setup. Multilingual SEO is about reaching users who speak different languages. This means creating multiple language versions of a site, for example an English version and a Spanish version, so the content is available to speakers of each language, regardless of their location.
International SEO targets specific regions or countries. It doesn’t need multiple languages but rather content tailored to the preferences of users in different geographic locations. For example a business might have an English language site for users in the US and UK, each optimized for regional keywords and cultural differences.
An International SEO Strategy Should Cover Everything
You need to think about everything from country-specific domains to keyword research in multiple languages. Following multilingual SEO best practices is crucial to ensure your strategies are effective and avoid common pitfalls.
If you’re just getting started with global SEO, it’s important to focus on one country or language at a time (it’s better to start targeting by region, but more on that later.)
You can use multilingual SEO services to target multiple countries and languages simultaneously, but that’s not necessary for everyone.
The first step in optimizing your site for your international audience is to have a strategy in place before you get started.
Just like with everything else related to SEO, the process can be complicated.
So, if you don’t know what you’re doing, you can get lost quickly.
But, to build a strategy, you need to figure out where your current traffic is coming from.
Some businesses may have a large global audience, and they should start the research with that country first.
Other important elements to remember: be consistent with your content, plan, and keywords.
Planning Your Multilingual Website
Planning a multilingual website requires careful consideration of several factors, including your target audience, languages, and content strategy. Here are some key steps to help you plan your multilingual website:
Identify Your Markets
Identifying your target markets is crucial in planning a multilingual website. You need to determine which countries and languages you want to target, and what type of content you want to create for each market. Consider the following factors when identifying your markets:
Language: Which languages do your target audiences speak? Understanding the primary languages of your audience helps in creating content that resonates with them.
Country: Which countries do you want to target? Knowing the specific countries allows you to tailor your content to meet regional preferences and regulations.
Culture: What are the cultural nuances and preferences of your target audiences? Cultural understanding ensures your content is relevant and respectful, enhancing user engagement.
Competition: Who are your competitors in each market, and how can you differentiate yourself? Analyzing competitors helps you identify gaps and opportunities to stand out.
By thoroughly researching these aspects, you can create a multilingual website that effectively reaches and engages your target audience.
Conduct Keyword Research for Multiple Languages
Conducting keyword research is essential in planning a multilingual website. You need to identify the keywords and phrases that your target audiences use to search for your products or services in each language. Here are some tips for conducting keyword research for multiple languages:
Use keyword research tools: Utilize tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to conduct keyword research for each language. These tools can help you find relevant keywords with high search volume.
Identify long-tail keywords: Focus on long-tail keywords that are more specific and less competitive than generic keywords. These can help you attract more targeted traffic.
Use native speakers: Collaborate with native speakers to ensure your keywords are culturally relevant and accurate. Native speakers can provide insights into local search behavior and language nuances.
By conducting thorough keyword research, you can optimize your multilingual website for search engines and ensure it meets the needs of your diverse audience.
Country/Multi-Regional Targeting and URL Structure
If your website explicitly targets audiences in different regions, it is called a multi-regional website.
This type of targeting works best for a company that has a reason to be in each of these countries separately.
For example, many e-commerce business sites that offer different products focus on country targeting first.
Make sure your content is unique for different regions, so you’ll prevent canonical issues on your site.
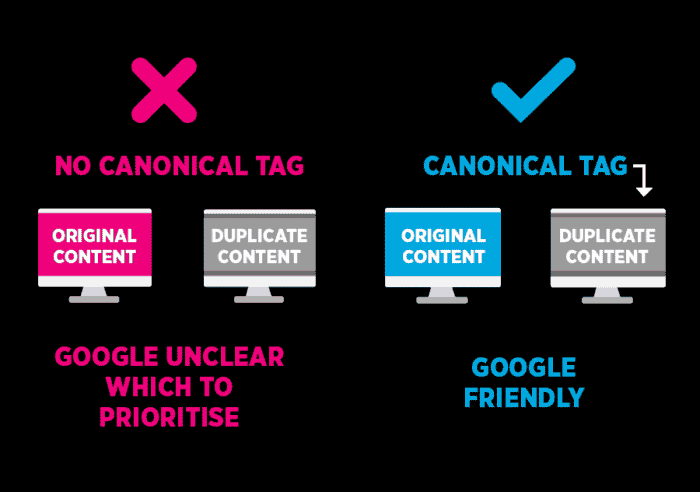
It is even more important than language targeting because it plays a key role in the customer’s decision-making process.
When a customer is looking for a product from your online store, he or she will only be able to find it from your website if it is listed in his/her country.
This means that you must ensure that your products and content are available in the correct countries and languages.
Using ‘link rel alternate’ for hreflang tags is crucial in this context. It helps search engines serve the correct version of your content based on users’ language and regional preferences, avoiding duplicate content penalties across translated pages.
However, if there’s not enough organic search volume to target a specific country, you can start by targeting the language instead.
This way, you can get a little bit of traffic traction and then migrate to your preferred country-targeted approach.
What to Keep in Mind When Targeting According to Regions?
In this case, ccTLD is the strongest structure that sends indications to users and search engines where your targeted audience is located.
If you have a website with a domain extension .uk like www.mybusinessname.uk, then users and search engines will recognize that this website is targeting people who live in the UK.
However, this doesn’t mean that your website won’t rank or drive traffic from other countries as well.
Also, it doesn’t mean that if you don’t have ccTDL, you can’t rank in a specific country.

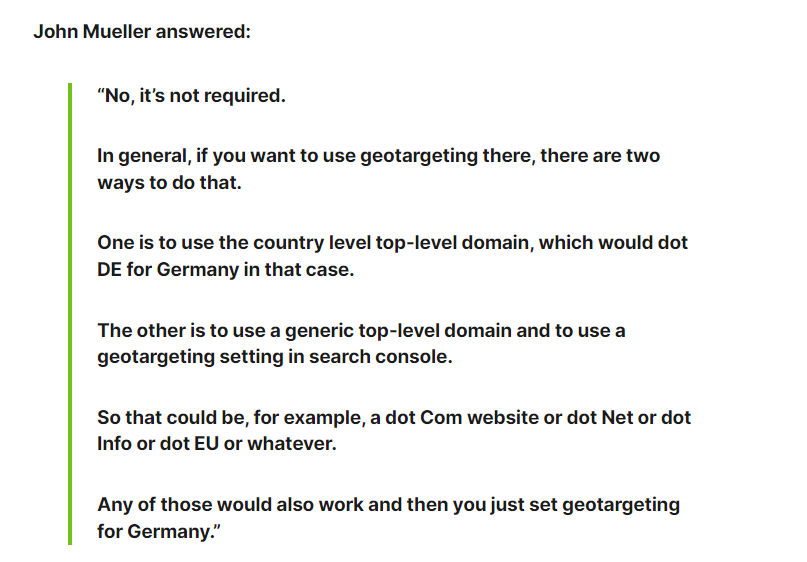
Using ccTLDs to target more than one market/country works perfectly for any business that has
Enough resources to develop localized content for each country
A substantial potential market to target different users
Enough time to build your website authority from scratch
Depending on the business, it may be a bit expensive to host and maintain each domain.
Language Targeting
If your services are the same worldwide, you should probably just focus on language targeting.
Optimizing content for native language speakers is crucial for effective multilingual SEO, as it enhances user experience and improves organic search visibility.
As you can guess…
A multilingual website is one that offers content in more than one language.
For example, a US business that has both English and French versions of its site.
In this case, Google tries to find pages that match the searcher’s language.
For example, Skype offers the same product to all its users.
So, despite the country of origin, it focuses on language rather than the country on its homepage.
What to Keep in Mind When Targeting According to Languages?
If you don’t have a reason to show different content to different locations (or don’t want to let users switch between this content), language targeting is usually easier.
You should go for a language-targeted approach when the location of your audience isn’t an essential factor that can influence services/products, content, and website goals. Multilingual website SEO strategy is crucial for reaching a global audience by optimizing website content in multiple languages, increasing visibility in search results, and driving traffic and sales.
It allows you to keep all your communications within one website, saving time and money.
You can choose from two URL structures: subdirectories or subdomains, if you want your SEO efforts to pay off.
If you are not sure, don’t worry.
You can start with a language-targeted approach and move towards a country-targeted approach as you identify enough activity from a specific country.
Technical Optimization for Multilingual Websites
Technical optimization is critical in ensuring that your multilingual website is search engine friendly and provides a good user experience. Here are some key technical optimization strategies for multilingual websites:
Choosing the Right URL Structure
Choosing the right URL structure is essential in technical optimization for multilingual sites. Here are some options to consider:
Subdomains: Use subdomains to separate each language version of your website. For example, es.example.com for Spanish and fr.example.com for French. Subdomains can help in organizing content but may require more effort to build domain authority.
Subdirectories: Use subdirectories to separate each language version of your website. For example, example.com/es for Spanish and example.com/fr for French. Subdirectories are often easier to manage and can benefit from the main domain’s authority.
Country code top-level domains (ccTLDs): Use ccTLDs to target specific countries. For example, example.co.uk for the UK and example.de for Germany. ccTLDs clearly indicate the target country to both users and search engines but can be more costly to maintain.
When choosing a URL structure, consider the following factors:
Search engine optimization: Which URL structure is more search engine friendly? Subdirectories often benefit from the main domain’s authority, while ccTLDs provide clear geographic targeting.
User experience: Which URL structure is more user-friendly and easy to navigate? Subdirectories and subdomains can be easier for users to understand and navigate.
Maintenance: Which URL structure is easier to maintain and update? Subdirectories are generally easier to manage, while ccTLDs may require separate hosting and maintenance.
Remember to use a consistent URL structure across all language versions of your website, and to use hreflang tags to indicate the language and regional targeting of each page. This ensures that search engines can correctly index and serve the appropriate language version to users.
By carefully planning and optimizing your multilingual website, you can enhance its visibility in search engine results pages and provide a better experience for your international audience.
What If You Want to Target Both by Language and Country?
Well, it’s doable, but the cost can be pretty high.
That’s only advisable when you get enough traffic from different locations, which calls for a more hybrid approach.
Many multinational brands have found the best ways through trial and error, so here are some tips if you want to follow in their footsteps:
Geotarget first based on the country.
If you’re going to target multiple languages and countries, use subdirectories.
Use hreflang to send users to the appropriate language page.
If you want to take a language targeting approach, focus on translation.
If you want to take a country targeting approach, focus on the localization of different page elements.
Feature your international websites in their own URLs and under their relevant web structure.
Additionally, ensure that you link relevant internal resources within the same language to improve user navigation and assist search engines in understanding page relationships.
Conclusion
When it comes to global SEO, there are a few schools of thought.
You could also use multilingual SEO services to target multiple countries and languages at once.
Ultimately, the decision of which route to take depends on your specific goals and needs.
But no matter which path you choose, remember that an effective global SEO strategy is key to reaching a wider audience and driving more traffic to your site.





