Website Ranking Issues: What’s Holding Your Site Back
What’s holding your website back from top rankings? In this article, we’ll look at the six most common website ranking issues that may be hindering your efforts. Frequent Google algorithm updates can significantly impact your website rankings, so it’s crucial to stay informed about these updates through reliable SEO sources.
This information is important because recent studies have shown that 75% of people don’t scroll past the first page of a Google search. A Google ranking dropped dramatically can be due to various factors, including over-reliance on specific ranking factors like backlinks.
Here’s we talk about how search engines work and what you can do about to rank higher and bring more organic traffic.
How Search Engines Work
Search engines are intricate systems designed to sift through the vast expanse of the internet to find and rank the most relevant information for users. This process involves three main stages: crawling, indexing, and retrieval.
Crawling is the first step, where search engines deploy software programs known as “crawlers” or “spiders” to scour the web for new and updated content. These crawlers follow links from one page to another, much like a digital spider weaving its web, ensuring no stone is left unturned.
Once the content is discovered, it moves to the indexing stage. Here, the crawled content is organized and stored in massive databases called indexes. Think of this as a giant library where every piece of content is cataloged and ready for retrieval.
The final stage is retrieval, where the search engine pulls relevant information from its index in response to a user’s query. This is where the magic happens—algorithms evaluate the indexed content based on factors like relevance, authority, and user intent to present the most pertinent search results.
Search Engine Crawlers and Indexing
Search engine crawlers are the unsung heroes of the internet, tirelessly working behind the scenes to ensure your content gets noticed. These software programs scan and index website content, playing a pivotal role in determining search engine rankings.
Crawlers navigate the web by following hyperlinks from one page to another, indexing the content they encounter along the way. This indexed content is then stored in vast databases known as indexes. When a user submits a query, the search engine sifts through its index to generate search results.
The ranking of these results is influenced by various algorithms that assess the indexed content’s relevance, authority and other factors. This means that the way your content is crawled and indexed can significantly impact your search engine rankings. Ensuring your website is easily navigable and free of broken links can help crawlers do their job more effectively, ultimately boosting your visibility in search results.
Website Architecture and Confusing Internal Links Structure
In short, your website architecture refers to how web pages are linked to each other throughout your website.
By correctly grouping different areas and keeping a consistent structure, users and search engines will better understand your content, which translates into better website ranking.
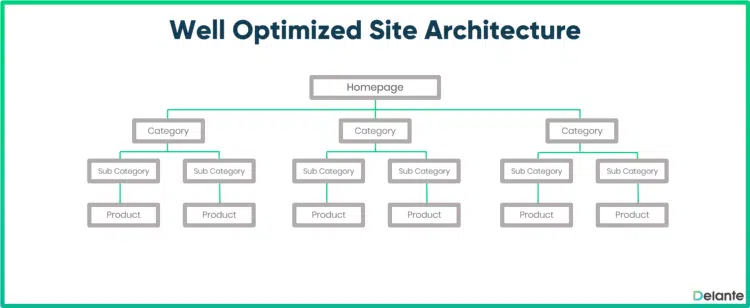
So, think about this…
If someone from Google or any other search engine were to view (visit) your website, would it be clear which page is most important?
Which page should that visitor focus on for maximum value?
And which pages are simply there for decoration or because you copied them from another site?
Also, keep in mind that there are several internal linking best practices you can implement to improve your on-page SEO. Internal links are crucial for enhancing content structure and user experience, but overuse can negatively impact search rankings, so a balanced approach is essential.
Poor Keyword Optimization
The cornerstone of search engine optimization is keyword optimization.
But if you are choosing keywords that are too general or have low search volume, you could be missing out on a lot of potential traffic.
While using keywords is important, overloading your page with keywords (keyword stuffing) can harm your rankings.
And it may take time for you to see significant gains from low-search-volume keywords, but it will eventually happen.
To choose relevant, targeted keywords, analyze and discover which keywords and terms people are already using to find information about your business and industry.
Then use free SEO tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs, or other keyword analysis tools to identify more phrases that should be included in your SEO strategy.
Follow a thorough keyword research strategy for your target audience. Take help from the Google Search Console to understand your visitors better. Google Analytics can also be instrumental in monitoring user engagement and site performance metrics, such as bounce rates and session durations, to improve your SEO.
Keep in mind that long-tail keywords have click-through rates up to 6% greater than regular keywords.

Also, beware of keyword cannibalization as it may impact your domain or website ranking position.
Broken Links and Poor-Quality Backlinks
Broken links on your website send a message to search engines that there is something wrong with your website, which may penalize your site in ranking.
And poor quality backlinks that are irrelevant or manipulative send the same message to the Google algorithm.
Broken links can also negatively affect your Google rankings, making it crucial to address them promptly.
The solution?
Take a close look at every link on your website using a backlink checker, get rid of any broken ones, and make sure all of them add value and relevance to each web page they’re linking to (especially the homepage).
This is why cleaning up bad links is one of our most important recommendations for improving website ranking.
Unoptimized Title Tags, Meta Descriptions, and Headings
Title tags, meta descriptions, and headings play a significant role in how search engines understand your page’s content. Unoptimized tags can confuse search engines, leading to lower rankings.
Title Tags: Ensure your title tags are descriptive, under 60 characters, and include target keywords.
Meta Descriptions: These should summarize the page content concisely while compelling users to click.
Headings: Use relevant H1, H2, and H3 tags to structure your content for both users and search engines.
Poor Formatting and Grammar Issues
Long paragraphs, improper formatting, and grammar mistakes can disrupt the user experience, leading to higher bounce rates and lower rankings. Break up text into smaller paragraphs, use bullet points where appropriate, and ensure your content is grammatically correct.
Use shorter paragraphs to improve readability.
Bullet points or numbered lists can make information more digestible.
Proper grammar ensures clarity and professionalism, improving user trust.
Unclear Search Intent
Although search is a major traffic source, not all keywords are equal.
You need to rank for high-volume and low-competition keywords (more on that in a bit), and you also need to be specific with which terms people use when they search.
You must get clear on who your customers are and what they are looking for when searching.
That’s how you will learn exactly what type of content to write or how to structurize your website.
Understanding user search intent can help ensure that visitors turn into leads and leads turn into customers. This understanding is crucial as it can significantly influence your search rankings.
Duplicate and Thin Content
If you have duplicate content on your website, each version will be listed separately in Google’s index, and each version can potentially get its own page rank.
The issue is that a lot of websites today—particularly ones created by automated processes—are filled with hundreds or thousands of pages that look nearly identical.
These thin pieces of content essentially suck up space in Google’s index and provide no real value to readers, stealing potential website ranking from more valuable, original, and quality content. This can lead to google rankings dropped, as search engines may penalize sites with duplicate or low-quality content, impacting overall search engine performance.
Missing Alt Text or Broken Images
Images are a key part of search-optimized pages.
It’s vital to ensure that all relevant images on a page have alt text filled in.
Alt-text is used by screen readers, which read webpages aloud to visually impaired people, and is also used by search engines as a description of images.
Let’s say you have a graphic on a page of your website, such as an infographic or a chart.
If that image doesn’t have alt text, Google or any other search engine will be unable to use it when people search for terms related to it.
The same is true if you have an image that’s broken in some way, e.g., one that’s corrupted and can’t be displayed by browsers.
If Google sees images with missing or broken alt text, it may penalize you for not making sure everything is crawlable – meaning your website ranking may be hindered. This can negatively impact your visibility in Google search results.
Website Speed and Responsiveness
In the fast-paced digital world, website speed and responsiveness are critical technical SEO factors that can make or break your search engine rankings. A slow and unresponsive website not only frustrates users but also sends negative signals to search engines, potentially harming your rankings.
Google recommends that websites should load within 3 seconds to ensure a good user experience. To achieve this, you can optimize images by compressing them without losing quality, minify your code to reduce file sizes, use a content delivery network (CDN) to distribute your content more efficiently, and leverage browser caching to speed up load times for returning visitors.
Responsiveness, on the other hand, refers to your website’s ability to adapt to different screen sizes and devices. With the increasing use of mobile devices, having a responsive website is more important than ever. A responsive design ensures that users can easily access and navigate your site, whether they’re on a desktop, tablet, or smartphone.
By focusing on these technical aspects, you can improve user experience and send positive signals to search engines, ultimately enhancing your search engine rankings.
Conclusion
The best way to determine which of the above issues is hurting your website traffic would be to compare your site’s traffic with that of another site with similar content.
Take into account overall search volume and take a look at the top search results for your main keywords.
Are there any similar sites that outperform yours?
If so, what do they have going for them?
Content, better links, more inbound links, or something else entirely?
By comparing their performance with that of your own and your competitors, you should be able to get a good idea of where you can improve and boost your own rankings.





